
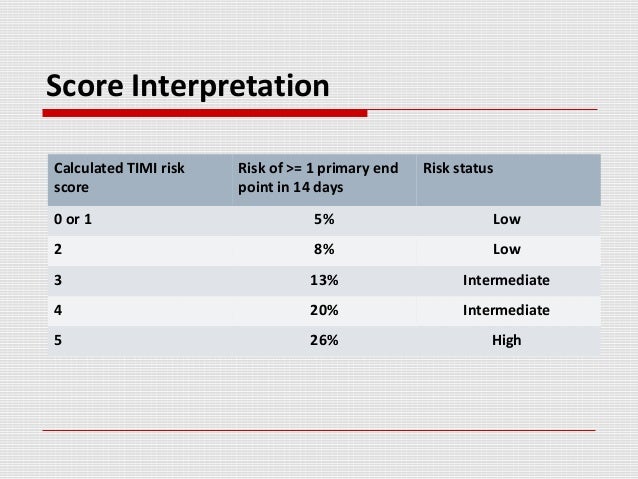
If an x-ray is done this should be in the Resus bay, except for stable low risk patients who may be suitable to leave the department for their x-ray, this will need to be judged on a case by case basis.This should not be allowed to delay any treatment measures, especially reperfusion therapies.In cases of LBBB urgent echocardiography may be useful, if readily available, to detect wall motion abnormalities (suggesting myocardial ischaemia) and hence assist in decision making.≥ 1 lead anywhere with ≥ 1 mm STE and proportionally excessive discordant STE, as defined by ≥ 25% of the depth of the preceding S-wave.≥ 1 lead of V1-V3 with ≥ 1 mm of concordant ST depression.≥ 1 lead with ≥1 mm of concordant ST elevation.Smith-Modified Sgarbossa Criteria can help if LBBB or paced:.Comparison with old ECGs will be useful.Minimal S-T changes can be difficult to interpret, especially in those with pre-existing CAD or other significant CVS disease.anatomical localisation of ST elevation.development of pathological Q wave and TWI.classic changes in acute myocardial infarction.New LBBB (LBBB should be considered new unless there is evidence otherwise).≥ 2.5 mm (i.e ≥ 2.5 small squares) ST elevation in leads V2-3 in men under 40 years, or ≥ 2.0 mm (i.e ≥ 2 small squares) ST elevation in leads V2-3 in men over 40 years.Left ventricular systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction 20 minutes) ECG features in ≥ 2 contiguous leads of:.Arrhythmias requiring treatment such as sustained ventricular tachycardia.Ongoing pain, or recurrent episodes of pain despite initial treatment whilst in the ED.Renal insufficiency (glomerular filtration rate 109 and 1).A small but still significant proportion (140.By definition this will be shown by an elevation of serum troponin levels in the absence of S-T segment elevation.Non-STEMI (Non S-T Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction) The ECG may show S-T segment depression or transient S-T segment elevation, but often will be normal.NSTEACS refers to any acute coronary syndrome which does not show S-T segment elevation.NSTEACS (non S-T Segment elevation acute coronary syndrome) New LBBB may be included in this sub-heading as the treatment approach is similar to STEMI.presentation with clinical symptoms consistent with an acute coronary syndrome together with S-T segment elevation on ECG.STEMI (S-T Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction) A “CODE STEMI” activation system should be in place in any hospital that has an acute percutaneous coronary intervention service.A clinician with ECG expertise should review the ECG.All patients who present with a suspected acute coronary syndrome must be assessed in the ED on an urgent (category 2) basis and have an ECG performed within 10 minutes of first acute clinical contact.Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a catch all term that refers to ischemic symptoms resulting from acute coronary occlusion.Coronary artery disease accounts for > 30% of death in West and presents acutely as acute coronary syndromes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
